Table of contents
Understanding enamel erosion and how it occurs will help you prevent this from happening. If you already have signs of enamel erosion, learn how to treat it.
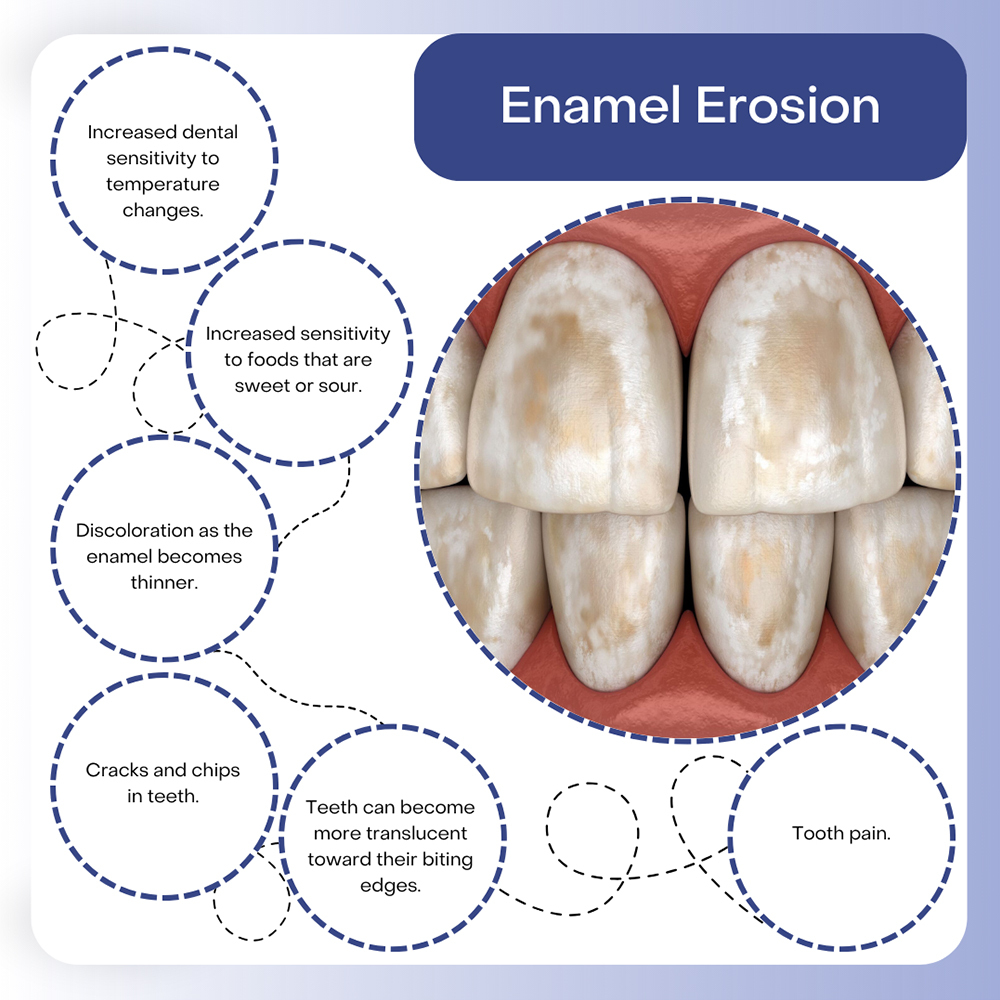
Tooth enamel erosion can cause symptoms that include:
Tooth enamel loss usually occurs because of exposure to acids in foods and beverages. It also occurs because of acid produced by bacteria found in dental plaque. Saliva is a protective fluid that continually works to help neutralize acids in your mouth, protecting your teeth.
Tooth enamel consists of calcium and phosphate, but some minerals are lost over time, weakening its structure. Their loss occurs when bacteria accumulate, producing acid that removes minerals from enamel during a process called demineralization. The same effect occurs if you eat something very acidic.
The process is partially reversed during remineralization, as some minerals remain in your saliva and are redeposited into your tooth enamel. Unfortunately, repeated exposure to these acids will result in enamel erosion over time.
Failing to brush your teeth regularly or consuming too many acidic foods and drinks will cause your enamel to become thinner and degrade gradually.
Foods that may cause enamel erosion under the right conditions include:
Other problems that can cause enamel erosion include:
If you are concerned you may have enamel erosion, please visit My New Jersey Dentist so we can quickly diagnose this problem and discuss how best to treat it.
Tooth enamel has no living cells, so it will not regenerate. However, several treatments are available for tooth enamel restoration and repair.
Suppose you have minor tooth enamel loss, where you have a soft spot in the enamel. In that case, we might be able to re-harden it using topical applications of professional-strength fluoride. Fluoride helps to reverse enamel erosion by replacing some of the minerals lost during enamel erosion, strengthening your tooth enamel.
If your tooth enamel loss is more extensive, we may suggest dental bonding. During treatment, tooth-colored composite resin is applied directly to the tooth surface, helping to seal and protect the tooth. Treatment is fast and inexpensive to complete and will hide any discolorations caused by tooth enamel loss.
If your enamel erosion is extensive, we may suggest protecting the tooth with a dental crown or veneer. A crown or veneer may be necessary if the erosion has resulted in tooth decay. Covering the tooth will help prevent the decay from worsening, restoring your tooth to full strength while ensuring it looks good and feels comfortable.
Preventive dentistry can help you maintain strong and healthy tooth enamel for longer. Some easy tips to follow are below.
See your dentist regularly for checkups and hygiene appointments. Removing hardened plaque, called calculus or tartar, removes bacteria that produce acid, protecting your tooth enamel. Dental visits allow our dentist to detect any signs of enamel erosion and provide appropriate treatment before the damage can progress.
Have you noticed signs of enamel erosion? Contact My New Jersey Dentist for a proper evaluation and discussion of how to treat this problem.

My name is Victoria Kushensky. I am a general dentist dedicated to remaining at the forefront of my field. Combining compassionate care with extensive knowledge, I offer cosmetic and general dentistry services as well as advanced root canal treatments.
I earned my Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the esteemed New York University College of Dentistry. Throughout my career, I have honed my skills in various dental procedures, ensuring effective treatment for each patient’s unique needs. I prioritize patient comfort and understanding, taking the time to thoroughly explain procedures and address any questions.
More about Dr. KushenskyMy NJ Dentist: Victoria Kushensky, DDS
385 Prospect Ave Suite 304
Hackensack, NJ 07601
(201) 298-8000